The most common plant diseases that occur on indoor flowers are described here. Attention: on any plants in case of violation of agricultural technology (bay, hypothermia, overfeeding with fertilizers) or when planting in uninfected soil, signs of several diseases may appear. In the world around us, not one or two types of microorganisms, but millions. We can guess the disease by single characteristic spots. There are specific diseases that cannot be confused with anything: gray rot (long threads of gray mold), powdery mildew (leaves seem to be covered with white dust), dropsy of leaves in succulents (pimples are green, the plant is not oppressed), ring patterns from viruses and some others.
But very often in plants several diseases appear at the same time, for example, in orchids tracheomycosis (fusariosis) and at the same time septoriosis or phyllosticosis. Root rot and alternariasis. The good news is that the fungicides we are offered in the store are usually effective against a variety of diseases. But do not forget that drugs of hazard classes 3 and 4 are allowed for personal households (i.e. for the house).
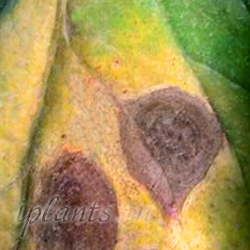
Alternariasis and dry spotting
The pathogen is fungi of the genus Alternaria. The fungus mainly affects leaves, sometimes stems and tubers.
Symptoms: Dry brown spots appear first, primarily on the lower and then on the upper leaves. Usually concentric circles are visible on the spots. As the spot increases, it gradually turns black, and gray conidia become visible on it.
Frequent temperature changes and humidity changes contribute to the spread of the disease, i.e. alternation of the dry and wet period. But the optimal conditions for the development of the fungus at temperatures above about 25-30 ° C and humidity up to 90%.
Prevention
Avoid thickening plants, cut out excess branches and leaves during. Ventilate the room or greenhouse, if the flowers are on the balcony, make sure that there is good ventilation and mold does not grow along the walls - this is an indicator of microclimate disorders.


Control measures
Fungicides used to combat alternariosis:
- abiga peak 50 g per 10 liters of water
- MC acrobat 20 g per 5 liters of water
- oxychom 20 g per 10 liters of water
- hom 40g per 10L water
- alirin-B 2 tablets per 1 liter of water
- vitaros 2 ml per 1 liter of water
Spraying three times after 10 days.
Anthracnose



The pathogen is fungi of the genera Colletotrichum, Gloeosporium, Kabatiella. Palm trees, ficuses, anthurium, etc. are more often affected.
Symptoms: the disease affects the leaves, stems, petioles and fruits of plants. Spots on different plants, and depending on the pathogen look different.
- Kabatiella zeae - causes the formation of small rounded or irregular spots, 2-5 mm in diameter with a clear outline. It looks like a yellow spot, with a brown or black dot inside. If the spot is larger, instead of a black dot, a dark rim forms, and inside it is a grayish ring.
- Colletotrichum orbiculare - causes the formation of usually reddish brown, often with a slight yellow border of spots, from 2 to 12 mm. On some plants, the spots are pale green. Rounded or elongated in shape. In the affected areas, the spots merge, dry out, become like parchment, crack, and holes form.
- Colletotrichum trichellum are large yellowish-brown or gray-brown spots on leaves and stems with dark sporulation pads. If you look closely, it is noticeable that on the spots on the upper side of the leaf, the surface is not smooth, but covered with fluffy spore hairs, but the spores are already noticeable with severe damage to the plant. On the fruits, the spots are gray-brown with a dark middle, depressed.
Anthracnose develops rapidly in greenhouse conditions, i.e. with high air humidity (about 90-100%) and an elevated temperature of 22-27 °. And also with frequent (several times a day) spraying of plants. The mushroom is frost-resistant - it is preserved in plant residues, in seeds and spreads with water when watered.
Prevention
Removing leaves with suspicious spots, disinfecting the ground, etching seeds. Suspicious plants bought in the store to quarantine. In case of signs of manifestation of the disease, it is necessary to stop spraying plants.
Control measures
Spray, usually three treatments are sufficient, using fungicides:
- 1% solution of Bordeaux liquid (100 g of copper sulfate + 100 g of lime per 10 liters of water, dilute strictly according to the instructions)
- oxychom 15-20 g per 10 liters of water
- copper sulfate: 100 g per 10 liters of water
- colloidal sulfur: 50-100 g per 10 liters of water
- stroby fungicide, in a system with other fungicides, 4 g per 10 L of water
- abiga peak: 50 g of suspension per 10 liters of water
Ascochitosis



The pathogen is fungi of the genus Ascochyta. The most severe lesions are caused by ascochitosis of chrysanthemums, which are most often affected by plants of the Asteraceae family.
Symptoms: at the initial stage, small, only 1-2 mm reddish or brown spots appear on the leaves, sometimes brown, reddish with a yellowish or brown rim, of different shapes. The spots increase in size and acquire a dark brown necrotic tint with a yellowish chlorose border along the edge. Small black spores of the mushroom can only be seen under magnification with a magnifying glass. If the growth of the fungus on the stem rings it, then the stem easily breaks.
Sometimes the disease begins with signs of drying out the plant - the tips of the leaves begin to dry out, a dark brown strip forms on the border with healthy tissue. The pathogen is very resistant to deep temperature changes, i.e. tolerates both severe drought and soil freezing. It is preserved on plant residues, seeds. The disease spreads with wind, non-disinfected soil, water drops.
Prevention and treatment, as with anthracnose.
Dropsy (Eden)
A disease not caused by fungus or bacteria, but resulting from waterlogging of the soil, often with a lack of lighting. It usually manifests itself in succulents, typical of peperomia, fat women, kalanchoe, possibly on pelargonium, scheffler.
Symptoms: in the plant, most often barely noticeable pimples appear on the underside of the leaf, they seem watery, but in fact they are dense, sometimes like cork growths, some look like warts, the color of the leaf can persist, i.e. the spots are green, they can acquire a gray necrotic color. This is due to the fact that some of the roots die off (from overfilling, waterlogging, hypothermia), nutrition is disrupted by conductive vessels that were supplied with these roots. Since the waterlogging is not strong, the soil managed to dry out, the decay did not spread further, but the spots remained. The affected leaves will no longer recover, but if good conditions are created for the plant, the new leaves will be healthy.
The difference between dropsy (edema) and other diseases, root rots is that the plant is not depressed, it grows noticeably, and the spots themselves in small areas affect 1-3 leaves on the bush. Leaves do not turn yellow with dropsy, do not dry out and do not fall off!
Treatment and prevention: Adjust watering, do not fill, after abundant watering and when compacting the soil in the pot, loosen the ground. Compose soil with a high proportion of draining, loosening particles - at least 1/5 or 1/4 part of the volume of the pot.
Downy mildew (Peronosporosis)



Pathogens - fungi of the genera Peronospora, Plasmopara, Pseudoperonospora, Mildew. The disease can affect any indoor plants, but the disease is quite rare.
Symptoms: yellow, then brown spots of irregular shape are formed on the upper side of the leaves, with a false powdery rose of cucumbers, the spots are angular (the specifics of the leaf structure). Gradually, necrosis occurs in these places, and the spots become brown. On the lower side of the leaves - at the beginning of the disease, a light gray coating from conidial sporulation of the pathogen, which came to the surface of the leaf through the stomata, then this coating gradually turns black. Diseased leaves turn yellow, become wrinkled or corrugated, wilt and dry. The pathogen with a strong degree of damage can penetrate the vascular system, which is noticeable on the section in the form of darkened vessels (mycelium and spores).
The disease prevails on heavy acidic soils. Exacerbates the spread of high humidity and poor ventilation. The source of infection is not disinfected soil and seeds.
Prevention
Maintaining low humidity, regular airing, thinning and cleaning of bushes. Soil change and disinfection. If signs of illness are already detected, avoid spraying and when watering water on the leaves.
Seed preparation for sowing :
- immersing them in hot water at 50 ° C for 20 minutes, followed by rapid cooling in cold water for 2-3 minutes
- soaking in a seed pickler, e.g. Maxim
Control measures
Removal of diseased leaves and severely affected branches. Preparations containing copper can be used: oxychome, cuproxate, 1% solution of Bordeaux liquid, order. These fungicides are more readily available (cheap and effective) for the treatment of garden and garden plants. You can get more modern drugs: quadris, bravo - but they are not sold in small packaging, they are intended only for agriculture (in cans and bottles), gardeners usually purchase them in collective purchases.
Fungicides are available for a simple florist:
- topaz 4 ml per 10 liters of water
- abiga peak 50 g of suspension per 10 liters of water
- oxychom 15-20 g per 10 liters of water, three times
Start treatment at the first sign of disease and repeat every 7-10 days, especially carefully treat the underside of the leaves. It is necessary to carry out at least 3-4 treatments.
Drugs: pure bloom, speed, cancer are ineffective against powdery mildew.
Powdery mildew



A common plant disease caused by fungi of "Podosphaera fuliginea," "Erysiphe cichoracearum" and "Oidium" species is powdery mildew on Oidium grapes.
Symptoms: at the beginning of the disease, small mealy spots appear on the flowers and leaves. They are easily erased, but then reappear and increase in size, become saturated gray. Gradually, the mycelium is compacted and becomes almost brown. Powdery plaque can be on both sides of the leaf. The leaves gradually dry out, buds and flowers crumble, the growth of the plant stops. The most favorable conditions for the development of the disease are increased humidity - about 60-80% and warm air in the range of 15-26 ° C.
Of the domestic plants, powdery mildew most often affects: laurel, senpoli, gloxinia, roses, gerberas, kalanchoe, etc.
Prevention
For the prevention of powdery mildew of indoor plants and flowers, sulfur pollination can be carried out 3-4 times per summer. Overfeeding plants with nitrogen fertilizers, especially during the budding period, increases the risk of powdery mildew disease. On the contrary, feeding with phosphorus and potassium fertilizers increases resistance to the powdery mildew pathogen. You should also ventilate the room more often, avoiding cold drafts. Pay attention to the bushes and trees that grow under your windows, if they show signs of illness, you constantly need to be on the alert - the fungus spores are easily carried by the wind.
In addition to sulfur treatment, prophylactic spraying with whey (reverse) can be performed. Ordinary whole milk is also suitable, but whey is preferable (fewer traces on the leaves), you need to dilute with water in a ratio of 1:3 and spray the plants. For prevention, repeat after 2 weeks.
Fighting powdery mildew at home
If powdery dew got on indoor flowers, and violets (senpoli), potted gerberas, indoor roses are especially susceptible, then you can use the same products as for garden plants, except for highly toxic (baileton), but preference should be given to fungicides such as topaz, speed.
You can use the preparations Chistotsvet, Skor, Rayok - all of them are available in small packaging, contain diphenoconazole, dilute 2 ml per 5 liters of water. For fruit trees, vegetables and berries, we breed 2 g per 10 liters of water, maximum 4 treatments: the first - on a green cone, the rest - after 12-14 days, stop processing 20 days before harvest.
It is quite safe to spray powdery mildew at home with a solution of soda ash and copper sulfate: dilute 10 g of soda ash and 2 g of soap (household, tar) in 1 liter of water, dissolve 2 g of copper sulfate separately in a glass of water. Pour the copper solution into the soda solution, add water to a volume of 2 liters of liquid and spray the plants.
If you heard from someone a recipe for fighting powdery mildew with antibiotics, do not try to repeat, penicillins, tetracyclines and other antibiotics do not work on fungal infections, in extreme cases, they will help against bacteriosis, but no more.
Drugs such as Topaz, Vectra, Hom, Oxihom, Bordeaux liquid (1%) can be used. How to get rid of powdery mildew on gooseberries, currants, roses and other garden crops - read more: Powdery mildew.
Helps as prevention and treatment spraying with iodine solution: dilute 1 ml of alcoholic pharmacy tincture of iodine in 1 liter of water. Roses can increase concentration - dilute 1 ml per 400 ml of water.
Septoriosis



The pathogen is fungi of the genus Septoria.
Symptoms: dark brown or dark gray spots with a yellowish border (on anthurium) or, as on azaleas, small reddish or reddish-yellow spots, which gradually increase. Then blackening appears on the spots in the center - the fruiting organs of the fungus, which can even overwinter on the leaves at subzero temperatures and the disease will begin to spread in the spring. Some forms of separiosis have different manifestations (depending on the type of plant):
- The pathogen is Septoria albopunctata - it looks like small 2-5 mm reddish-purple or brown spots with a gray center. With the development of the disease, the spots increase, and in the center of some of them you can see small dark brown or black spores of the fungus. Over time, the spots merge, brown, and the leaf dries up. Ideal conditions for the development of the disease are high humidity and temperature in the range of 28-31 °.
- The pathogen Septoria populi - the so-called white spot, first causes the formation of small whitish or gray spots with a brown rim along the edge, rounded or oval.
Prevention
Removing leaves with suspicious spots, disinfecting the ground, etching seeds. With signs of manifestation of the disease, it is necessary to stop spraying leaves, improve air circulation (ventilation).
Treatment of septoriosis
When the spots have already appeared and spread further, it is necessary to spray using chemicals: among them, a 1% solution of Bordeaux liquid, popular in gardening (100 g of copper sulfate + 100 g of lime per 10 liters of water, dilute strictly according to the instructions), a solution of copper oxychloride (xom, oxy), copper sulfate (100 g per 10 liters of water). As well as:
- colloidal sulfur 50-100 g per 10 liters of water
- strobies in a system with other fungicides, 4 g per 10 liters of water
- abiga peak 40-50 g per 10 liters of water
- fungicides: pure flower, speed, crayfish, discor, keeper - dilute any 4 mL to 5 L of water
- vitaros 2 ml per 1 liter of water
Repeat spraying after 7-10 days.
Grey rot



Pathogen - fungi of the genus Botrytis Botrytis.
Symptoms: most often, the affected places appear on the stems in the form of a fluffy grayish-olive coating. With further development, the disease passes to leaves, ovaries of flowers and fruits.
Over time, the lesion takes the form of dry rot with concentric spots. After a few days, the spot grows and rings the stem. For the first week, there is no sporulation of the fungus on the spot, it pales to a straw color in the center, blurred ring-shaped stripes become visible. Gray rot is similar to gray loose cotton wool or mold. Inside the stem, tissue necrosis develops, while the vessels die off, and the movement of water stops. The escape above this zone is withering.
The pathogen belongs to the so-called wound parasites, the infection spreads mainly with wind, dust, splashes of water, unwashed hands, etc. Also contributes to the spread of the disease poor lighting, high humidity, dense group fits, and the optimal temperatures for the development of the disease are 17-25 ° C.
Prevention
Preventive measures include soil disinfection during transplantation (heating in the oven or microwave), regular ventilation of rooms, removal of dying leaves and thinning seedlings, good lighting. Avoid waterlogging the soil, especially with cool maintenance, if flowers are on the balcony early in spring or in late summer - in autumn. When transplanting, trichodermin, barrier, barrier or phytosporin preparations can be applied to the soil (spill the soil).
Control measures
At the first sign of the disease, remove diseased leaves and inflorescences. Dust the affected area with charcoal powder, chalk or wood ash. You can make a paste from the trichodermin preparation (moisten a small amount of powder with water) and also coat the affected areas. Spraying with topsin-M solution (0.1%) or phytosporin solution (dilute to tea color). In case of severe damage, spray:
- fundazole (0.2%)
- copper-soap solution: 0.2% copper sulfate and 2% household soap
- fungicides: pure flower, speed, crayfish - dilute any 4 mL to 5 L of water
Repeated treatments are carried out in 7-10 days.
Sooty fungus

It appears in the form of a dry sooty film on aucubes, bugs, laurels. It is caused by the fungus Capnopodium, which settles on the secretions of aphids, whiteflies, mealybugs. Plaque itself is not dangerous to the plant, but it clogs the stomata on the leaves, thereby disrupting the breathing process. The plant slows growth and weakens.
Control measures: timely spraying from pests that form sweet secretions (aphids, shields, thrips). After healing from diseases, wipe the affected plants with a sponge soaked in soapy water, rinse with warm, clean water, treat with phytosporin: take a liquid or paste and dilute in a glass of water to the color of weak tea. Spray the leaves.
Sometimes sooty fungus settles on the surface of leaves affected by other fungi, carefully examine the nature of the spots, quarantine the plant.
Leaf rust



The pathogen is rust fungi, for example, of the genus Phragmidium or Puccinia.
Symptoms: expressed in the appearance of orange-brown tubercles on the upper surface of the leaf, sometimes yellow or red round spots. On the back of the leaf, pustules are clearly visible - pads (like warts) oval or round. Gradually, the spots grow into stripes, the leaves turn yellow and fall.
Prevention
The disease provokes uneven watering and high humidity, but even with good care, infection is possible at home through garden flowers in cut or with new potted plants bought in the store, for example, gerberas. Infection can also get with garden soil, because rust often affects apple trees or pears.
Control measures
Remove affected leaves and branches. Apply fungicide spraying:
- abiga peak 50 g per 10 liters of water 1 g
- byleton per 1 l of water
- vektra 2-3 ml per 10 l of water
- Bordeaux blend 1%
- copper vitriol 10 g per 1 liter of water
- oxychom 15-20 g per 10 liters of water
- order 20 g per 5 liters of water
- strobe
- topaz 4 ml per 10 liters of water
- hom 40g per 10L water
Repeat the treatment 2-3 times after 10 days. Biologics do not help against rust: phytosporine, bactophyte, etc.
Phyllosticosis (brown spotting)
The pathogen is fungi of the genus Phyllosticta. Of the home flowers, hibiscuses, roses, orchids, etc. are susceptible to the disease.
Symptoms: small dark reddish or dark purple dots appear on the affected plants at first. They enlarge and turn into brown spots with a purple, almost black border along the edge. The middle of the spot thins, dries out and falls out in plants with non-skinned leaves, holes are formed. When viewed through a magnifying glass, black rounded spores can be seen in the brown areas of the spot. The disease spreads with wind, non-disinfected soil, water drops.
Phyllosticosis of orchids manifests itself in small spots about 2 mm in diameter, dark brown in color, slightly depressed, holes do not form, often the disease is called "black spotting," since the leaf is dotted with small spots like a rash - the spots do not merge into large ones, remain scattered, but the leaf turns yellow, and then the spores of the fungus become noticeable. The disease spreads quickly enough, as orchids are often in an atmosphere of high humidity.
Prevention
Compliance with the rules of care and hygiene - timely watering, if necessary, but not more often, pour water only under the root, water should not fall on the root neck, in the axils of the leaves. Use only warm water for irrigation, without chlorine and salts (iron, calcium). Make sure that the plants have enough light, weakened chlorous leaves are more susceptible to infection. Ventilate the house or rooms, avoiding drafts. Ventilation should be very good - an indicator of proper ventilation - the absence of mold in the bathroom, the perimeter of the window frame, the corners of the rooms. Observe the temperature regime, take into account the species requirements of orchids and other plants - deviation from the norm and habitual care weakens the immune system.
Treatment of phyllosticosis
- vector fungicide - dilute 2-3 mL of the drug to 10 L of water
- abiga peak - 50 g per 5 liters of water
- stroby - 4 g per 10 liters of water
- oxychom 20 g per 10 liters of water
- fungicides: pure flower, speed, crayfish, discor, keeper - dilute any 1 ml per 1 liter of water
- vitaros 2 ml per 1 liter of water
Spraying at the appearance of the first signs of the disease or preventive, then subsequent with an interval of 7-10 days. In some plants, you can safely remove the affected leaves (for example, in hibiscus), in orchids do not rush to cut out the affected areas to healthy tissue, this can further weaken the plants. You can cut the sheet only when it is already very yellow. Otherwise, treat by spraying.
Root rot



This is a group of diseases caused by a number of pathogenic fungi of the genera: Pythium, Rhizoctonia, Phytophthora, etc. All these diseases sooner or later appear on the crown, tops of plants, but infection begins through the root system. If the pathogen is serious, and the plant is young (cutting, seedling, seedlings), then the leaves do not even have time to start turning yellow - the roots and the lower part of the stem quickly rot.
Orchids, senpolias, cacti and succulents are most susceptible to root rot. The reason is a violation of agricultural technology.
The black leg is a scourge of seedlings, manifested in the decay of the lower part of the shoot, the handle. The rot is the most typical - blackening, softening of tissues. A very part of the black leg is striking when the soil is waterlogged, poor aeration, if the clumps of the earth are so dense that there is a constantly anaerobic environment around the roots. The source of infection is not sterilized earthen mixtures, inventory, pots and seating boxes after sick plants.
Phytophthora
It is a type of root rot. In this case, the plant first slows down growth, fades somewhat, the leaves lose color, become pale, only then the roots rot and the plant dies. The first impression with this disease is that the plant does not have enough water, but after watering the turgor does not recover, and the leaves wither even more. In plants with dense leaves, the leaves do not wilt, but are covered with brown extensive spots that begin from the central vein.
Prevention
Pick the right soil for your plants, add more porous, draining materials so they structure the soil. Do not use fine river sand or sand from the children's sandbox (quarry) - it cements the earth mixture! Use small pebbles with a particle size of 3-4 mm, which can be bought in specialized departments and aquarium stores, or sift river pebbles. When planting, add Gliocladin to the pot with the plant
Make sure that the soil does not become waterlogged, water after the permissible degree of drying: if it is indicated that the watering is plentiful, then in the pot the earth should have time to dry by about 1/2 or 1/3 of the top of the pot. If you immerse your finger in the ground, you will find that the soil is dry on top, and a little wetter (cooler) inside the pot - then you can water it.
If moderate watering is recommended for the plant, then the soil should dry out completely - if you immerse your finger in the pot inside, it should also be dry (the finger does not feel that it is cooler, wetter). Of course, you should not stick your fingers in the ground before each watering. Just wait until the soil dries from above and wait another 2-3 days, before watering, so that it has time to dry in the depths. And if it suddenly got colder and the temperature dropped, you may need to wait even longer - 5-7 days before the next irrigation.
To propagate houseplants, cut off only healthy cuttings and leaves. Be sure to sterilize the land for planting cuttings, especially if you breed plants that are very susceptible to blight and root rot (for example, gesnerium, gardenia, scheffler). Old, already used pots in which plants died must be scalded with boiling water.
Soak the seeds in a pickle before planting, use, for example, the drug maxim.
Control measures
With a large development of root rots, when a significant part of the roots died out, and most of the shoots drooped, lost their elasticity, treatment is useless. If the tip of the petiole or twig is blackened at the root, it can be cut off, dripped into the water of phytosporin and put back on rooting.
If the plant has signs of wilting, the raw soil must be urgently removed from the pot. Rinse the root system, remove rot. If healthy roots are still preserved, process them (soak for a few minutes) in a fungicide solution:
- Alirin B - 2 tablets per 10 L of water
- gamair - 2 tablets per 1 liter of water
- Order 5 g per 1 liter of water
- pre-energy 3 ml per 2 liters of water
- bactofit 10 ml per 5 liters of water
- oxychom 10 g per 5 liters of water
- hom 20g per 5L water
- vitaros 2 ml per 1 liter of water
Spottiness
This is a whole group of diseases that have both fungal and bacterial nature.
Pathogens - fungi of the genera Ascochyta, Colletotrichum, Phyllosticta, Pestalotia, Septoria, Vermicularia, etc. Spotting refers to diseases whose causative agent is difficult to identify, it can be anthracnosis, septoriosis, phyllostictosis, ascochytosis, but the characteristic of the spots is not expressed. At the same time, brown spots appear on the leaves of the plant, which grow in size with the spread of the disease, merge and affect the entire leaf. If the plant is strong enough, resistant to diseases or is very well looked after, the spots grow slowly and the leaves dry out also slowly.



Spot prevention
Contribute to the development of diseases violation of conditions of detention. This waterlogging is especially aggravated by hypothermia of the root system (after watering with cold water or when transporting from the store home during the cold season). Spots can also develop in warm, humid conditions, especially with poor air circulation and planting in dense clay soil.
Avoid large crowding of plants and excessive watering. Regularly ventilate the room, greenhouses and provide good lighting. For prevention, water the plants with a solution of the drug phytosporin-M or bactophyte. Can be added to pots when planting a tablet of gliocladin.
Control measures
In garden conditions, you need to collect and destroy any plant remains with stains from dead plants. In house flowers, trim the affected leaves and branches. Apply spraying with fungicides that can cope with most fungal infections.
- abiga peak 50 g per 10 liters of water
- MC acrobat 20 g per 5 liters of water
- oxychom 20 g per 10 liters of water
- hom 40g per 10L water
- alirin-B 2 tablets per 1 liter of water vektra 3
- ml per 10 liters of water
- benomyl (fundazol) 1 g per 1 liter of water
- 1% solution of Bordeaux liquid (100 g of copper sulfate + 100 g of lime per 10 liters of water, dilute strictly according to the instructions)
- copper sulfate: 100 g per 10 liters of water
- vitaros 2 ml per 1 liter of water
At home, indoor flowers from spots should be tried to treat with more affordable and simple means: use Chistotsvet, Skor, Rayok preparations - all of them are produced in small packaging, contain the same active ingredient - diphenoconazole, you need to dilute 2 ml per 5 liters of water. Spray the leaves with the solution, repeat after 2 weeks. Add zircon (6 drops per 1 liter of solution) to the solution of these fungicides Chistotsvet, Skor, Rayok.
Red burn
Pathogen fungus of the genus Stangospora Staganospora. A disease characteristic of hippeastrums and some bulbs.
Symptoms: red narrow spots appear on the leaves and peduncles, on which spore-bearing crusts subsequently form, scales completely redden in the bulbs. In a sick plant, deformation of leaves and flowers begins, flowering does not begin or stop, bulbs rot.
Treatment
Treatment of bulbs in fungicides. You can use the drug maxim (soaking bulbs), but it can cause burns to the buds of leaves and peduncles - their tips have a very thin epidermis. The third photo is burns from the drug Maxim, although the bulbs are cured, the burns will remain.
You can also treat the red burn of the hippeastrum with other fungicides:
- fundahol (benomyl) 1 g per 1 liter of water
- vitaros 2 ml per 1 liter of water
- oxchom 4 g per 1 liter of water
Read more about Hippeastrum Rot Treatment and Forum Discussion Red Burn
Black spotting



The pathogen is fungi of the genus Rhytisma, Dothidella.
Symptoms:
- Rhytisma acerinum - causes the formation of large rounded spots, initially yellowish and vague. Then black dots appear on them, which gradually merge and form black shiny stromas (influx), surrounded by a yellowish border. Sometimes there may be no yellowing around the black stroma.
- Rhytisma salicinum - causes similar lesions, only spots are more convex, more angular in shape, large and small.
- Rhytisma punctatum - causes the appearance of small, dotted or teardrop-shaped, shiny black and convex stroma.
- Dothidella ulmi - causes the formation of grayish-black, rounded stroma; they are convex, initially shiny, later - rough, like warts.
A combination of conditions contributes to the spread of the disease: increased humidity, shading and high temperatures.
Control measures
Spraying with fungicides:
- abiga peak 50 g per 10 liters of water
- MC acrobat 20 g per 5 liters of water
- benomyl (fundazol) 1 g per 1 liter of water vektra 3
- ml per 10 liters of water
- oxychom 20 g per 10 liters of water
- hom 40g per 10L water
- alirin-B 2 tablets per 1 liter of water
- vitaros 2 ml per 1 liter of water
Spraying three times after 10 days.
Tracheomycosis
Tracheomycoses are a group of diseases, the so-called vascular wilts - pathogens enter through the roots and infect the vascular system of plants, clog the lumens of blood vessels with their mycelium, secrete toxins, the plant does not receive water and nutrients and begins to wilt.
Tracheomycosis includes such diseases as:
- verticillosis (verticillosis)
- fusarium wilt (fusarium)
- malsecco in citrus
The symptoms are very similar, all diseases are diagnosed only in laboratory, all are incurable, are found at the stage when pathogenic fungi have already poisoned the vascular system, this is something like blood poisoning in animals. Orchids, phalaenopsis, dendrobiums, cattleias, etc. are especially affected by tracheomycosis. From other indoor flowers: fuchsia, roses, balsamine, begonias, geranium; from garden: petunia, carnations, chrysanthemums, asters, dahlias. Vegetables are prone to tracheomycosis: cabbage, celery, cucumbers, tomatoes, peppers, eggplants, lettuce, melons, potatoes, pumpkin, radishes, rhubarb.
There are also tracheomycosis-resistant plants: senpoli, ageratum, gypsophila, mallow, periwinkle, primrose, zinnia, asparagus, ferns, philodendrons. Of the vegetables, only corn and asparagus can withstand.
In foreign practice, all tracheomycosis wilts are simply called: wilt - from wilt - wilt.
Verticillus wilt



The pathogen is fungi of the genus Verticillium. It reproduces exclusively asexually - conidia, infects plant roots and poisons xylem tissues: it grows and reproduces systemically throughout the plant.
Symptoms: at the initial stages of the disease, the lower leaves acquire a grayish-greenish color due to the development of mesenteric necrosis. The leaf tissue between the veins turns brown and dries. Then wilting begins, most of the leaves, starting from below, turn yellow, curl and dry. On the cut of the stem, browning of blood vessels is noticeable. Vascular lumens are filled with thin multicellular mycelium. Plants lag behind in growth, develop poorly, then die. Sometimes the disease manifests itself on the plant in the drying and dying of individual branches of the bush. If the conditions are favorable, then the disease goes to other branches and the whole plant dies quite quickly. If there are unfavorable conditions for the development of the fungus, then the disease can drag on for months and part of the plant looks healthy, and part dies.
The pathogen persists in the soil in the form of microlocies for several years. The optimal temperature for germination of sclerotia is 25-27 °, humidity is 60-70%. The fungus is most likely to develop on soil with a neutral pH = 7-7.5. Spores of the fungus germinate and penetrate the conductive tissue, where mycelium develops, causing blockage of blood vessels. Since there is a gradual clogging of blood vessels from bottom to top, the wilting of the leaves begins with the lower leaves and gradually covers the entire plant.
Prevention
Do not use garden land for indoor plants without preliminary processing: pour on a baking sheet with a layer of 5 cm, warm up at a maximum temperature of 20 minutes. Disinfect the seed with warming and pickles (for example, fungicide maxim)
Control measures
Due to the peculiar biology of the pathogen (development in the soil and spread through conductive vessels), chemical agents are ineffective. Treatment is possible only in the initial stages, by spraying with fundazol, vectra (3 ml per 10 l of water) or topsin-M at a concentration of 0.2%.
Fusarium (fusarium wilt)



The pathogen is fungi of the genus Fusarium.
Fusarium fever develops only on weakened plants primarily in dying areas. The course of the disease can pass by the type of tracheomycosis wilt or with rotting roots. Plants are affected at any age. The fungus is found in the soil and enters the plant through soil and wounds, with water from natural sources, a non-sterile tool during grafting or pruning. Contributes to the spread of the disease increased humidity and soil.
Symptoms: In young plants, the disease manifests itself in the form of rotting roots and root neck. In these places, the tissues turn brown, the stem becomes thinner, the leaves turn yellow. The tops of the shoots wither in the affected plants (loss of turgor), and then the whole shoot. This happens, as in the case of infection with verticillosis, due to the blockage of blood vessels by toxins and enzymes secreted by fungi. Therefore, the darkening of the vessels is also visible on the cross section. But sometimes tracheomycoses appear only on part of the crown, the rest remains healthy for the time being - then at a bush or tree they are depressed, individual branches droop. If you cut (cut clean without darkening) cuttings from healthy branches during, you can root and get a healthy plant.
The speed of the disease depends on how favorable the conditions are for the development of the fungus. With high soil and air humidity, as well as temperatures above 18 ° C, the disease can destroy the entire plant in a few days. If the humidity is lowered, then the disease can turn into a chronic form, then the plant slowly wilts within 3-4 weeks.
Control measures
Removal and destruction of the plant along with a lump of earth. Disinfection of pots with 5% copper sulfate solution, bleach, or at least scalding with boiling water.
If wilting has just begun, then you can try to treat the plant with fungicides:
-
vektra 3
- ml per 10 liters of water
- benomil (fundazol) 1 g per 1 liter of water for orchids can be 1 g per 100 ml
- Alirin B 2 tablets per 1 liter of water
- vitaros 2 ml per 1 liter of water
Spraying three times, with an interval of 7-10 days.
How to treat orchids: get rid of the old substrate (throw it out, or cook the bark for at least half an hour). Cut rotten roots. Prepare a solution of the fungicide, and spray thoroughly the root system and leaves. Leave to dry. Plant in a fresh substrate (large pieces of bark, foam, cork). Do not spray, water with immersion if necessary for a short time (5 minutes is enough). It is advisable to keep sick orchids at a temperature of 23-24 ° C, without drafts, in very intense but diffused lighting (you can under lamps).
The soil for large plantings (growing seedlings and transplanting tuberous plants) can be prepared by pouring it properly with a solution of manganese (pink), Fitosporin-M, Maxim, or by adding trichodermin. When working, sterilize tools - knife, scissors and even garter material (wire, threads) with alcohol.











