 Overfeed with fertilizers - the stem cracked.
Overfeed with fertilizers - the stem cracked.The causative agents of cactus diseases are bacteria, fungi and viruses. Some diseases can be easily cured, while most cause significant damage to health and lead to the death of plants. Sometimes the symptoms are so inaccurate and proceed in a latent form that it is not possible to determine the disease.
Therefore, it is much easier to prevent diseases than to cure patients, especially when the cactus is not alone, but a whole collection. Preventive measures are strict adherence to the conditions of keeping and hygiene of plants.
 This cactus was frozen, cold air was blowing at it from a gap in the frame.
This cactus was frozen, cold air was blowing at it from a gap in the frame.Unfortunately, in most cases, cactus diseases end sadly. The plant either dies or will be mutilated. And still, most cacti torment two questions "why?" And "how to treat."
Even after all the repeated explanations that in most cases the cause of diseases is a violation of the conditions of detention, people cannot believe that only once opened (in the evening in cold weather) the unfortunate cactus can become covered with rusty spots and the like. But in fact it is. Even a seasoned cactus player suffers losses from his fleeting mistakes. Only compliance with all conditions, attention and prevention can prevent the occurrence of diseases.
The fact that the cactus "got sick" is not always immediately visible. Most often they forget that:
- opened the window in the evening in cool, windy weather;
- poured cold water on the cactus;
- that any wounds, cracks and cuts should be sprinkled with sulfur or crushed coal; cactus
- must be accustomed to the bright sun gradually, even the most sun-loving;
- that cacti need cool and dry wintering.
If the cactus fell ill, first of all, you need to remember and analyze what violations could be in the conditions of detention, whether you did everything right.
Sometimes illness, pest damage or the result of care errors is not immediately visible. How to understand that something is "unhealthy" for a cactus, something bothers him - just be attentive. You should worry about the cactus in such cases:
| External features | Possible causes |
|---|---|
| If there is no visible growth of the cactus (only in the spring-summer period) | The lack of plant growth in spring or summer is the first sign of some kind of trouble. The reason for this can be absolutely any: a disease or pests, or a mistake in care - first of all, a lack of light, rearrangement of a cactus to a new place, an incorrect transplant, pouring cold water, etc. After vaccination, as it causes a stressful situation. After too long and intense flowering, there may also be a slowdown or cessation of growth due to cactus depletion. |
| If the stem shrinks or shrinks | If the stem is hard to the touch, then first of all it is necessary to exclude the lack of moisture in the soil (i.e. watering, the soil is dry), especially if the cactus is in intense lighting. If the stem, on the contrary, is soft, then the reason is most likely in excess of moisture (the soil is damp), at this stage the plant is rarely saved, you can try an urgent transplant with the removal of all decayed roots. |
| If there is a change in the color of the stem or leaves | This is a fairly common reaction to changing conditions. When rearranging the cactus to a new place. With a change in illumination (with too bright light, lightening or redness of the stem and leaves can occur). When water gets on the stem or leaves (if the plant does not tolerate it). Some cacti are genetically based on a certain change in color with age. In some diseases, the color of the stem and leaves can also change, most often yellowness, browning and mosaic color appear. |
| If leaf or bud shedding occurs | This may be the first reaction to a stressful situation caused by changes in the conditions of detention. Rearrangement to a new place or even because the cactus turned the other side to the light source. If lighting, watering or temperature changes unexpectedly. For example, poured cold water. If the transplant is not carried out on time or not correctly. From the mismatch of micro- and macronutrients in the soil. This can also happen with diseases or pest damage. |
| If shoot death occurs | This occurs most often when roots are damaged when transplanted or watered with cold water. From a sharp drop in temperature or exposure to draft. This can also happen with diseases or pest damage. |
| If various spots or yellows appear on the skin | This is possible from the ingress of water on the stem or leaves (if the plant does not tolerate this). From exposure to sunlight, an untrained cactus can get sunburn. From exposure to cold air, the formation of rusty spots on the stem is possible. With a lack of nutrients in the soil, yellowing is possible, which takes place after feeding with mineral fertilizer. Yellowing or spots also appear in various diseases and pest damage. |
| If wounds or cracks appear on the cactus | This can be caused by mechanical injuries. With an excess of organic matter in the soil, the cactus grows intensively, and the skin cracks and bursts. |
| If root damage or decay is detected | The reason for the decay of the roots should be sought primarily in the waterlogging of the soil. Especially when there is a lack of light and low temperature. Root decay often begins with the fact that damage, cuts or wounds on the roots have not been treated with sulfur (which is needed for drying and disinfection). Insufficient moistening of the soil at high temperature and illumination can lead not to decay, but to the death of part of the roots. This is especially common when the pot overheats in the summer in the sun. |
| No blooms or short blooms. | A common reason is the lack of sunlight, the absence of cold wintering (resting period), any violation of irrigation and temperature regimes. Some cacti, on the contrary, do not bloom due to too intense or prolonged lighting. Wrong or untimely transplantation. Non-compliance of soil pH or its composition. Lack of nutrients in the soil or their excess. Repositioning the cactus to a new location or turning in place. Diseases and pest damage are also responsible for the lack of flowering. |
Cactus rot

Rot is the most common disease caused most often by disorders in care (excessive watering, cold wet wintering, etc.). Rot is caused by both fungal and bacterial damage.
The cactus phytophtora (pathogen of the fungus Phytophtora cactorum), for example, affects all parts of the plant, especially if there are lesions or wounds, but the root neck is most susceptible to the disease. Rot manifests itself, since we imagine it in the form of rot and the transformation of tissues into a sour mass.
Among the rots, it should be noted Helminthosporiosis (the causative agent of the fungus of the genus Pyrenophora) - a disease of crops - cactus trunks curve and dry out, and, moreover, in just a few days. Another disease of crops - rhizoctoniosis (the causative agent of the fungus of the genus Rhizoctonia) or wet rot manifests itself in darkening, blackening of the cactus stem, spreads through the vessels upwards. Both diseases can be avoided by disinfecting the ground for crops, etching seeds, and avoiding high humidity in the greenhouse.
Fusarium (the causative agent of the fungus of the genus Fusarium) should also be mentioned, which is detected suddenly - the cactus falls, the color of the cactus stem changes (becomes reddish, brown or purple). If you get the plant out of the pot, its roots break off, it can be completely rotten, depending on the stage. The cactus is poisoned by toxins released by fungi into the vascular system of the plant, which is noticeable on the section of the stem - a darkened clearly visible brownish ring.
Treatment of decayed cactus
If the rot affects the root system, then there are two options. The first - if the decay of the roots is only partially (in the very initial stage, usually discovered by accident) - all the affected parts of the roots are removed, and the rest are well sprinkled with coal powder or sulfur and the cactus is planted in fresh soil with a large proportion of sand. Watering only after three weeks is very careful. The second case, when the roots rotted completely, you can still save the upper part of the stem, rooted it like a stalk. In this case, part of the stem is cut off so that only healthy strong tissues remain. If decay of the root neck or stem has begun, then only the top of the cactus can be saved by grafting it onto another healthy cactus.
It happens that stem rot begins at the wound site on the skin of the cactus. If the place of decay is not yet large, then you can cut out the rotten tissues with a sharp knife, and this place is carefully sprinkled with sulfur. If the wound is small, then the scar will remain, and the plant will recover. But if the site of damage is significant, the cactus will be mutilated.
If the decay occurred on the top of the cactus itself, then it must be cut down to healthy tissue, and the cactus must be used as a stock for vaccination. You can disinfect all wounds on the body of a cactus with charcoal (you can crush a tablet of activated charcoal), gray, as well as green.

If you cut the top of the cactus to roost from a diseased plant, then prepare a disinfected substrate, which should be absolutely dry. Dry the cuttings of the cactus for a couple of hours in the air, sprinkle the cut with charcoal powder, then put it on the substrate, do not dig! The low crown of the spherical cactus cannot be fixed - it will not fall, and if the handle is unstable, fix it on several sides with large pebbles. No need to fill the entire substrate from above with gravel, a couple of stones are enough.
You can fix it differently. Stick a stick firmly into the ground, and tie the handle to it with a woolen thread. After that, do not water the cactus for at least 2 weeks. If it is a hot summer, i.e. high air temperature, then instead of watering, the cactus trunk is sprayed from a very small spray bottle, or only the air around the handle is pollinated and moistened. After 2 weeks, you can slightly moisten the soil in the pot not by watering, but by spraying, so that it remains wet for 2-3 hours, then dries. An unburied handle can always be lifted and see if new roots have appeared. If they appeared, then the cactus should be left alone (no longer raised), and the spraying of the earth should gradually increase.
Black rot (the causative agent of the fungus Alternaria radicina) - when black (dark brown spots) appear on the cactus trunk, in the form of leaks, moist, shiny and disgustingly frightening. The disease can spread very quickly. It is necessary to cut out all spots to healthy tissue. Spray the plant with fundazol, Oxyhom or Homom, and dry the cut points with sulfur.
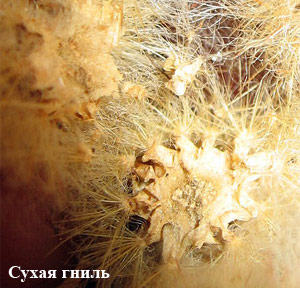
Dry rot (pathogen fungus Phoma rostrupii) or Fomoz - in the direct sense of decay is not observed, just so it is customary to call this disease. It is dangerous because when it is discovered, it is usually too late. Outwardly, the cactus pales slightly, and begins to dry out imperceptibly. If you cut the stem, the cactus will be dried inside. Since this disease is fleeting and methods of combating it have not yet been invented, the plant dies. However, it is possible to prevent the disease by periodically doing preventive spraying or watering with a systemic fungicide.
Spotting - their nature is very diverse, most of them are caused by viruses and bacteria, the appearance of which was facilitated by the conditions of detention. This is primarily exposure to cold draft, especially in winter or cactus damage in high humidity and cool air.

Rust on the cactus is one of the varieties of spotting, the stem is covered with rusty crusts or stains. The causes of the disease may be: sunburn; ingress of water (especially cold) on the stem; sudden decrease in ambient temperature; spores of pathogenic fungi; contaminated soil. The bad thing is that once they do, these rusty spots start to appear on other parts and spread more and more. Control measures:
- first of all, it is necessary to remove such a cactus from other plants in order to prevent possible infection;
- carefully remove the affected areas with a clean knife or blade disinfected with alcohol;
- treat with fungicides: Fitosporin, Topaz or Fundazol; further
- ensure good ventilation and avoid excessive watering. Water the cactus only when the soil is completely dry;
- if rust continues to spread, transplant the cactus into fresh, sterile soil, removing any old residue.
Very often you can see that by buying, for example, a sick cactus with unidentified spots and putting it at home in a well-lit place, in the heat, the spots do not increase, new ones do not appear. This happens often, especially when affected by fungal diseases. Any mushrooms do not like the combination of heat (dry air) and light. Once on a sunny windowsill with moderate watering, the cactus recovers on its own.
But if in a warm sunny place on the stem of a cactus, reddish or whitish spots appear and spread, sometimes similar to mica, it's a matter of a tick, which likes such conditions...
Brown spotting, or anthroknosis (the causative agent of the fungus of the genus Gloeosporium) - in cacti it manifests itself in a completely different way from on other plants. Spots of light to dark brown appear on the cactus stem, anywhere, both laterally and on the crown. The spots are dry, depressed, forming a dry crust. Spots slowly increase, capturing ever larger areas. Fight the same way - cutting out affected areas and treating with fungicides.
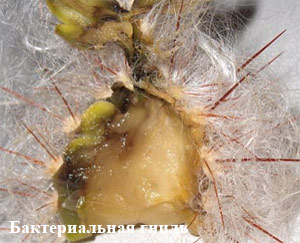
Brown rot (the causative agent of the bacterium Erwinia) - darkening of the cactus stem occurs, as a rule, from the root neck or from any other place (for example, if there was mechanical damage to the cactus skin and the causative agent of the disease got into it). At the same time, the cactus itself becomes soft to the touch, and gradually changes color to dirty brown. After a while, when the cactus breaks, you can see a slimy kisellike mass. As a rule, it is not possible to save the cactus - bacteria and their toxins quickly poison the entire plant.
Yellowing - the cause can be both a lack of nutrients in the soil and a bacterial or viral disease. Yellowing usually begins at the ends of shoots and the top of the cactus. First of all, you should eliminate the lack of nutrients and feed the cactus with mineral fertilizer - if the reason for this yellowing passes. General yellowing can also be caused by a virus, the so-called "jaundice," to fight the disease, there are no ways. It can pass fleetingly, and can last for many months or even years. Moreover, if you take an absolutely healthy-looking stalk from an infected plant, then after a while, it will be covered with yellowing.

Viruses in cacti
Viruses are much less common on cacti than they are supposed to be. In fact, as on other plants, viruses have characteristic features, which allows them to be identified, except when the body of the cactus is densely covered with spines and it is impossible to clearly see the manifestation of the pattern. And the pattern in viral diseases is always traced.
As a rule, these are concentric rings, various spots that have a certain sequence of manifestation on the stem, for example, the entire trunk of the cactus seems to be speckled - it is very similar, as if acid was splashed on it. Some people think it is sunburn after spraying, but it turns out that the plant was not sprayed or it did not stand in the sun. Spots, as a rule, are light - in this place there is no chlorophyll in the cells. And only artificially supported cacti infected with the virus in culture have a solid beautiful stem color - red, yellow, white, etc. - this is a genetically fixed disease.
By the way, it is the vaccinated cacti that are most often affected by viral diseases.
If you have a suspicion that the cactus has become infected with a virus, then you can try the use of antiviral drugs sold in a pharmacy for people, for example, remantadine (1 tablet per half liter of water).

A case from the life of the forum: "As I saw the gymnocalicium, I bought it right away (although I promised to buy the Dutch). Now I don't know to plant it, throw it away, because, in my opinion, there is nothing to re-root there, since they are relatively small. They are all wrinkled at the roots below and some have some sores. There were five of them in one pot of different colors. Maybe it's okay..."
In fact, these cacti did not grow, although the roots, as you can see in the photo, are healthy. So, in addition to the fact that in the dug cactus it is quite natural that the lower part of the stem may lose color (the process of photosynthesis does not go, and it becomes yellowish-brown), in addition to the fact that for many species it is natural to test the lower part due to contact with water, earth and lack of light, this cactus has a fungal lesion, as evidenced by an unevenly spreading patch of yellowing, as well as brown spots-crusts
The fact that the roots are healthy gives hope that the plant can be cured, wait for a new growth, and then re-root the top in order to get rid of ugliness. Hom, Oxihom, Fundazol or Quinozole can be used for treatment. Dilute the fungicide according to the instructions and bathe the cactus in the solution. Then take a new soil mixture, sterilize it (for example, withstand about 30 minutes in a very hot oven, after that it should be absolutely dry, cool).
Then plant a cactus and put under diffused light. After 3-4 days, depending on the air temperature, pour the fungicide solution. Repeat stem treatments in a week. If the cactus was in a period of rest, it will have to be woken up - rearranged in a warmer and lighter place, start drip irrigation. In general, cacti are taken out of hibernation by starting regular spraying from a small sprayer. But if a fungal or bacterial infection has appeared on the cactus, spraying can make the problem worse. Therefore, it is more correct to start a little watering. You don't need to feed with fertilizers, spray with zircon or epin! Stimulants will not help, and there will be enough nutrients in fresh soil. If there is enough light (you can put additional artificial lighting), the treatments have been carried out, such a cactus has significant chances to recover.
How and how to treat cacti
All rot, spotting, fungal or bacterial origin is aggravated in conditions of high humidity. I.e. dangerous at the time of illness any spraying (with the exception of solutions of fungicides), wet weather outside, etc. If you, for example, fight a flat or spider mite on a cactus by spraying (with or without insecticides), reduce watering! The temperature is of secondary importance, but the most severe lesions if the plant was in coolness and high humidity.
It is very difficult to establish a fungal or bacterial disease affected the cactus, most often there is still a fungal lesion. Bacterial rot is characterized by the formation of muddy mucus, often with an unpleasant odor (but this is already at the last stage, when the plant is almost all affected) and the transience of the disease. Bacteriosis can literally destroy a plant in a day.
Fungal diseases spread at different rates and depending on the conditions, if cacti stand on the balcony and rainy weather stands at this time, then the disease progresses. But even if the spots and other types of lesions (darkening at the root neck) do not increase and do not spread further, it is advisable to treat the cactus with a fungicide.
Fungicides work against fungi and bacteria, they are powerless against viruses. Again, there is a specificity. For example, the systemic fungicide "Maxim" is effective for root rot and root neck rot.
Some use a drug such as Fitosporin to control and prevent rot, it should be noted that it is very unreliable when the plant is already sick. You may not see any improvement, it is worth hoping only for stronger drugs.
When spots and rot appear on the cactus trunk, on the side or on the crown, spraying with drugs such as Hom, Oxich, Bordeaux mixture, fundazol, topaz is effective. Against some fungal diseases, such as brown spotting, coloid sulfur helps. It is not diluted in water as written in the instructions for use, but dusted with a paint brush.
Fungicides for the treatment of cacti
Of the chemical preparations for the treatment of cactus diseases, Kaptan is used - an organic fungicide, a substitute for Bordeaux liquid, used in the form of a solution (0.3-1%) for irrigation and treatment with a brush, or in the form of a powder by the method of powdering (insoluble in water). This drug is effective against many fungal and bacterial diseases, but does not work on mealy mushrooms. It cannot be used with lime (because it hydrolyzes in the presence of alkalis).
Fundazol is also used to combat pathogens of various diseases. It is used in the form of a solution (0.005-0.1%). Stems and roots are sprayed or brushed with it. Operating fluid is not stored.
Sulfur - to combat fungal diseases and tick. Sulfur is an insectofungicide. It is used in the form of an aqueous solution, but sulfur is not soluble in water, it is only wetted. Therefore, it is more effective to dust plants with a gray brush.
Quinozole is a drug for protecting plants from diseases caused by phytopathogenic fungi (contact fungicide-etch). Available in powder form. Quinozole is used against fungal, as well as bacterial rot. If you do not find this drug in a gardening store, you will find it in a pharmacy. For humans, quinosol is marketed as an antimicrobial. It is necessary to crush the tablet into powder and thoroughly dissolve it in 1/2 cup of water. Moisten the cactus trunk with this solution and pour the ground under the root. It can also be used to disinfect the soil and etch seeds. Operating fluid is not stored.
Maxim is a drug for protecting plants from diseases, a etcher. Used for seed dressing and soil disinfection (from fusarium, fomoz, wet rot, etc.). The difficulty may be that root rot appears from waterlogging and excess watering, albeit with Maxim's solution, is impossible - it is necessary to let the soil dry well. Dilute 4 ml of the drug in 50-100 ml, spill the soil with this solution, soak the seeds, and moisten the trunk and leaves of the cactus with a brush or sprayer. The duration of action of the drug is about 10 weeks after treatment. Operating fluid is not stored.
Topaz - the drug is used to protect against powdery mildew and rust. 1 ampoule is diluted with 5 liters of water. The action time is about 2 weeks. At least 3 treatments are required.
Hom (copper oxychloride) is a means of fighting diseases (Phytoflorosis, macrosporiosis, brown spotting, anthracnose, rust, various bacterioses and spotting). One of the most effective drugs against diseases of cacti, succulents and other plants. 20 g of powder are diluted per 5 liters of water. Spraying is repeated as needed up to 5-6 times. The duration of action of the drug is about 2 weeks. The working solution is not stored.
Phytosporin is a biofungicide for protecting plants from fungal and bacterial diseases. In fact, this drug is effective only at the initial stage of the disease. Opinion of many growers: Phytosporine should be used only when there is no other fungicide at hand and for tillage after sterilization by heat treatment - i.e. as prevention. To prepare the solution, the paste at the tip of the knife is diluted with 1 teaspoon of water. Then take 4-5 drops per glass of water and water the ground or spray the plant.
Seed etching and soil disinfection before planting cacti (seeds and adult plants) saves seedlings from diseases. If against pests it is enough to thoroughly steam the soil, warm it in the microwave oven, in the oven, on water vapor, then this is not always effective from mushrooms and bacteria, and freezing is completely useless.
Therefore, it is advisable to spill the steamed earth before sowing seeds, transplanting cacti with a solution of a fungicide, for example, fundazole or quinozole. After that, of course, let it dry.