It is usually easier to fight pests of cacti than with diseases, but they cause considerable harm, sometimes irretrievably destroy valuable specimens. The result of damage by any pests is a slowdown or suspension of growth, lack of flowering or dumping of buds and flowers. A little later, various spots or plaque similar to a crust, sticky streaks, grains, blackened or bleached areas, etc. appear on the stems of cacti.
Ticks on cacti
The most common pests of cacti. They differ in microscopic size and are difficult to immediately notice. Herbivorous ticks are many species, the red flat tick is most dangerous. The female tick is about 0.3 mm brick-red in color, with an angular-ovoid body. Males are rare, and it is almost impossible to notice them - they are even smaller. Eggs are bright red 0.1 mm. Larvae are broadly oval in shape, red, with three pairs of legs. As a result of a red tick lesion, spots appear on the cactus stem, as if covered with a rusty coating. There are no cobwebs. The bad thing is that the affected parts of the plant, covered with spots, remain disfigured.






Control measures. Ticks are not insects, but arthropods, so ordinary insecticides do not work on them. Acaricides are needed to destroy ticks. The problem is that many ticks develop resistance to poisons very quickly. Pests that survive the first treatment may be resistant to repeated ones. Therefore, at the first sign, it is better to use a strong drug right away. It can be an actellic, neoron, fufanon, apollo, oberon. Dilute the drug according to the instructions. It is advisable to carry out two treatments with different drugs with an interval of a week. For more details see acaricides. How to treat: spray the cactus stalk with acaricide solution and water the soil, even in the basal zone.
As a prevention against ticks, it is effective to wipe the cactus stem with a brush moistened in a solution of alcohol and acetone, the ratio is 2:1, or garlic and onion tincture. Read the full article on ticks on houseplants and control methods on the Herbivorous ticks page.
Scales
Pests have an oblong (oval in outline) body, from 2 to 5.5 mm long, usually gray, with more or less pronounced white hairs. Many legs are clearly visible on the sides of the body. There are viviparous species, like Spilococcus cactearum - the cactus worm itself, there are those that lay eggs. The female oviposition is carried out in white fluffy cocoons, similar to lumps of cotton wool.
Females and larvae harm plants. Worms are dangerous because they can be discovered too late. Among the pests there are many species that have different preferences. Some usually settle in the roots and basal zone - worms of the genus Rhizoecus are small, up to 3 mm adults, when they breed strongly, they can also be seen on the stem. But most species of worms are surface pests, mainly concentrated in the areoles, between the papillae and ribs of cacti, as well as in the basal zone. Shelter worms are especially fond of - at the very beginning, hits are hidden in the upper layers of the soil, between the stems of cacti, if they grow in a group. When they begin to multiply intensively, they crawl over the entire surface of the cactus. The movements of the worms are slow, but noticeable movements.
Outwardly, small shaggy white bodies of pests look like lumps of cotton wool, foam crumbs, in the basal zone as if sprinkled with flour or similar to a white salt coating. It is bad that cacti lag behind in growth, the stems pale, lose intense green color. In some species, for example, in mammilaria, the stems lose weight, thin, and become sluggish. With severe damage, cacti can die. Very often, worms come to our house with purchased cacti, so take a closer look at newcomers.
Control measures. It is best to deal with worms with systemic drugs - a solution of actara or confidor is poured over the soil. The active ingredient from the solution is absorbed by the roots, and the juices of the plants become poisonous to pests. If the worms are concentrated locally - on the roots and neck, root baths can be used. For this purpose cactus roots up to root neck are maintained in hot water with temperature 50-55 ° C during 15 minutes. You can rinse the roots in the actellic solution, but the effect of the drug should not be long.
Here's what experienced florists recommend, Colleague:
- It is necessary to thoroughly rinse the roots from the worm. Under hot water - start in warm and gradually remove cold. There will be nothing for the cactus, and the worm will boil. Not a single white speck should remain!
- Lather Fairey's roots. hold in foam. Rinse thoroughly.
- Dip the roots in a solution of phytoverm - very strong, like thrips. Hold for 15 minutes.
- Dry the cactus.
- Throw out all the infected land, pour boiling water over the pot, wash with a comet.
- Plant the dried cactus in a new earth, into which add 2 packages of crushed activated carbon, perlite and vermiculite.
- Process (spill) the entire collection with phytoverm.
- Put the cactus back in place.
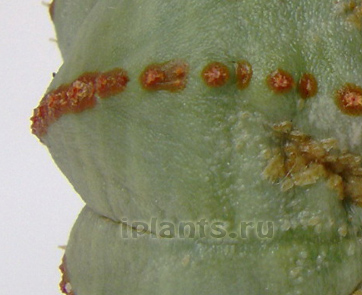
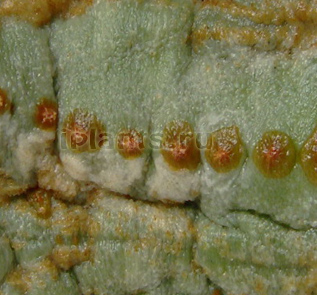
Shield and false shield

These pests are much less common on cacti than ticks or worms. The scutes are visible on the cactus stem in the form of small, only 1-2 mm flat scales. The colour is rufous to dark brown and the scutellum is stiff. False shields differ in that even older individuals have a more transparent or pale body, from gray-yellow to light brown. The essence does not change - these creatures drain cacti, suck out cell juice, bringing the plant to complete death. The shields move very slowly, for our eye they sit motionless in one place. If there are many scutes, the cactus stalk is covered with their sticky secretions.
Sometimes the scutes can be confused with brown spots formed by fungal or bacterial infection. In this case, try to skim the spot - if it is a shield, a wet spot remains from it, but there is a whole skin under it. If it is not possible to knock off the shield - a spot in the tissues of the epidermis, then this is not a shield, but some kind of disease and not an insecticide is required, but a fungicide.
Control measures. The shields must be removed from the stem with a cotton swab dipped in alcohol, if the spines allow. If the spines are very thick, it is better not to touch the insects, but to pour the cacti with a solution of actara or confidor. These are systemic insecticides - the pests will die, dry out, and they can simply be shaken off with a brush. Sometimes one treatment is enough, but it is advisable to repeat watering with an actara in a week.
Root nematode
These are worms of microscopic sizes - no more than 0.5 mm long, translucent, can be seen only under a microscope. Nematodes are quite rare, they prefer moisture-intensive, loose and nutritious soils. The problem is that it is difficult to detect immediately. Signs: delay and stop in growth, change in color of tissues - stems become paler, sluggish, thinning of the top of the cactus. The main sign is the appearance of spherical swellings or growths (galls) on the roots:

Control measures. All affected parts of the roots are cut off, the whole plant is treated with alcohol, and a hot bath is arranged for the roots. For this purpose cactus roots cleaned from the ground to root neck are dipped into hot water with temperature about 70 ° C for 30-60 seconds. Or hold at 50 ° C for 15 minutes. After the root bath, the entire root system is sprinkled with crushed coal. If we talk about chemical preparations, it is believed that agents based on imidacloprid are effective against nematodes - these are Confidor (1 gram per 5 liters of water), Tanrek, Vermitek. Immerse the plants in the solution completely and completely and the roots and stem. The nematode can be prevented from appearing on a healthy plant by sterilizing the substrate. In any way - steam in boiling water, heat in the oven or microwave.
Any disease and the appearance of pests is much easier to prevent than to treat. There are special hygienic procedures that should become mandatory for a novice cactus, especially if the cactus is not one, but several, or a whole collection. Hygienic procedures include regular spraying of cacti from a very small spray bottle, disinfection of planting containers, transplant tools, vaccinations, pickings, etc. Sterilization of soil and sand before transplantation. Alcohol is used to disinfect the tool, for lack of it, it can be replaced by simply scalding boiling water. Pots and plates are washed and also poured with boiling water. Soil and sand are roasted in the oven, or spilled with a solution of manganese.
All wounds on the stems or roots of the cactus caused by pests, or after removing part of the roots, are sprinkled with crushed coal or sulfur.

