Diseases caused by bacteria and viruses do not always have a clear picture, it is possible to mix signs of diseases, for example, oily or glassy spots may appear on the leaves with root rot, as with bacterial spotting, which then turn brown.
Bacterial rot



The pathogen is bacteria of the genera Pectobacterium, Erwinia.
The disease manifests itself in softening and decay of individual areas on the leaves, petioles, roots and fruits of the plant. Bacteria release the enzyme pectinase in the leaf tissue, which causes tissue breakdown. Most often, juicy and fleshy parts of plants are affected .
The leaves first appear a small shapeless spot, gray, brown or black, which grows in size. On bulbs and tubers, simply put, decay begins (mucus, oiliness), often accompanied by an unpleasant odor. Under conditions favorable for the pathogen - in a warm and humid climate, the disease spreads very quickly. And the affected part or all of the plant turns into a sour mass.
- The pathogen penetrates mechanical lesions on the plant - even microscopic cracks and wounds. It is preserved in soil with plant residues. Therefore, soil disinfection is required before planting, and when pruning roots, tubers and bulbs, sections must be sprinkled with crushed charcoal. And disinfect the tool with alcohol after each circumcision.
The development of the disease is provoked by the introduction of excessive doses of fertilizers, stagnation of water in the soil, dense, caked soil, cooling of moist soil in pots, for example, in a cool room in winter.



Bacterial spotting, bacterial burn, vascular bacteriosis



The pathogen is bacteria of the genus Xanthomonas, Pseudomonas.
The disease more often affects young leaves and shoots.
Bacterial spots, depending on the type of pathogen, have different symptoms. The most characteristic picture is when small watery spots first form on the surface of a leaf or stem, which gradually acquire a black or brown color. Most often, the spots have an irregular angular or amoebic shape, and are limited to a yellow or light green border, sometimes glassy or oily. The bacterium spreads along the veins or near the wound surface (break, leaf crack, stem). Unlike fungal spots, bacterial spots never form concentric circles or small black dots - spores. The transience is different, sometimes the plant withers for a very long time, sometimes it quickly turns yellow and dies.
The optimal conditions for the development of phytopathogenic bacteria are a temperature of 25-30 ° and high humidity. The death of bacteria occurs only at temperatures above 56 °. Bacteria of the genus Xanthomonas are resistant to drying and can tolerate low temperature for a long time.
- A variant of bacterial spotting is the so-called bacterial burn, which is caused by bacteria of the genus Pseudomonas. In this case, not spots appear on the plants, but rather large shapeless areas of blackening, which then dry out. It looks as if this section of the sheet is burnt, charred. If the disease is accompanied by favorable conditions, then it develops very quickly, causing the death of the entire plant. Bacterial burn begins more often with young leaves, shoots and flowers. Bacteria enter plants through stomata or wounds, begin to multiply in the intercellulars of the leaf parenchyma. The incubation period for the development of the disease is 3-6 days depending on the temperature. Bacteria persist in the soil and on the seeds.
Treatment of bacteriosis, rot, spots
The plant can be saved if the bacteriosis has not yet affected the entire vascular system or is local in nature (for example, the rot began at the tip of the leaf). If the roots have rotted, then you can try to root the top (if this plant is rooted by cuttings). If the rot affects only part of the roots, and the aerial part looks alive, you need to try to save the plant: free the roots from the ground, cut off all the rotten ones, transplant them into dry prepared soil and pour the fungicide with a bactericidal effect:
- abiga peak 50 g per 10 liters of water
- MC acrobat 20 g per 5 liters of water
- oxychom 20 g per 10 liters of water
- hom 40g per 10L water
- alirin-B 2 tablets per 1 liter of water
- vitaros 2 ml per 1 liter of water
All working tools and pots must be thoroughly disinfected (spilled with boiling water), the soil must be steamed or heated in the oven.
As a prophylaxis, as well as for the treatment of bacteriosis on vegetables and berry shrubs (do not use poisons), use the treatment of plants with the biobactericide phytolavin or watering and spraying with phytosporin, trichophyte. When planting seedlings and houseplants, gliocladin tablets can be placed in the ground. At home on indoor plants, spraying and watering the soil with a trichopol solution is successfully used - crush 1 tablet of trichopol per 2 liters of water.
Prophylactics or biologics may not always keep plants safe from infections. Do not rely entirely on them. Plant health depends, first of all, on the correctness of care, the chosen irrigation regime, the composition of the soil, the timeliness, but not the excessiveness of top dressing. Sometimes plants are weakened by a completely insignificant (at first glance) detail - inappropriate acidity, excess fluoride in water or chlorine, unsuccessful transplantation with a break in the roots, contact with cold window glass in winter. All these moments are entirely in the hands of the florist.
Bacterial plant cancer
The pathogen is bacteria of the genus Pseudomonas (Pseudomonas syringae, Pseudomonas tumefaciens).



The disease affects fruit trees and shrubs (among garden crops, almost everything is susceptible, but more often apple and pear trees) in indoor floriculture is found on fruit exotics (kiwi, avocado, etc.) and citrus fruits. Bacteria - pathogens live in the soil and persist in it for a long time. Therefore, the disease spreads with uninfected soil, as well as with infected vaccination material.
- Bacteria affect the vascular system, causing on the roots, stems, trunks the formation of first cracks, blackening, deformation of tissues, then the development of tumors, which at times reach huge sizes of several kilograms. On fruiting trees on fruits, signs of the disease appear at first in small small rounded spots, first light, then blackening. Then bumps grow in their place, turning into ugly warts. In citrus fruits, spots and warts do not penetrate or grow inside the fruit, but disrupt their ripening and storage.
In nature, the spread of the disease is facilitated by low temperatures, strong winds and heavy rains. The saddest thing is that the disease develops slowly and it is possible to detect signs of damage after a few months, even a year after buying a seedling or a cultivated tree (in rare cases, the disease develops in a couple of weeks). Large doses of nitrogenous fertilizers contribute to the development of the disease.
Control measures
Measures to combat bacterial cancer are effective only if the lesion is local and the bacteria have not entered the vascular system of the plant. There are no drugs in the fight against bacterial cancer. The only reasonable recommendation is to destroy the plant, and so as not to infect the environment (for example, burn). As a preventive measure - disinfection of the tool (secateurs, knives) with a 1% solution of copper sulfate (100 g per 10 liters of water), soaking for 5-10 minutes. When transplanting plants, old pots need not only to be washed, but also thoroughly rinsed with boiling water inside and out.
The earth can be disinfected by heating in the oven - the bacterium dies at temperatures above 50 ° C. When working with a sick or suspicious plant, it is necessary to treat alcohol and hands so that when in contact with a healthy plant do not infect it. Although carriers can be insect pests. When transplanting, try not to damage the roots, and if this happens, then sprinkle the damaged place with crushed charcoal, breaks or cuts of wood - with a garden brew to seal the "gate" for infection.
When buying grafted citrus fruits, seedlings of fruit and berry trees and stone trees, carefully examine the plants. Concerns are those that have cracks in the bark, deformed, as if corrugated leaves and any growths, as well as small spots on the fruits.
If the plant is sick, what to do
Viral diseases of plants
Viral diseases do not always have a pronounced picture, especially at the beginning of the disease, they are easy to confuse with chlorosis - all viruses cause yellowing. But sometimes a viral disease can be accompanied by signs that put the florist in a dead end, for example, first the chlorosis of the leaves begins, then they crumble, and the trunk rotts. This picture is characteristic of diseases of psorosis and xyloporosis of citrus fruits - sometimes found in homemade lemons.
Mosaic disease


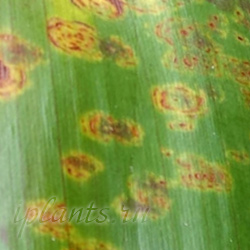
It is characterized by diverse in shape spots and stripes, white or yellowish on the leaves, light or dark on the flowers, which is caused by the decay of chloroplasts. A mosaic usually has a certain pattern - concentric circles, rings or stripes arranged in some order or pattern. In addition, mosaic is often accompanied by deformation of the sheet - wrinkling or curling. Begonia, calla, hydrangea, pelargonia, primrose are most often affected.



Sometimes the leaf virus is called jaundice - some viruses cause strong yellowing of the leaves or the color becomes light green. Individual shoots or the whole plant is stunted, the stems become brittle due to the fact that a lot of starch accumulates in them, the cells are literally clogged with them. At the same time, a mosaic pattern of concentric circles and spots can also be indicated on the leaves. Sometimes jaundice does not appear on the whole plant, but on a separate branch - leaf chlorosis begins, while new leaves may appear, but small and already chlorous.
But the curly leaves can cause fungal pathogens and viruses. With viral curly, numerous small spots 1-2 mm in size appear on the leaves, which then dry out, the leaves become wrinkled, shrink, and the flowers deform. The disease more often affects hydrangea (hydrangeas), primrose, pelargonia, poinsettia.
Control measures
The precise determination of a particular viral disease presents great difficulties. Direct control of viruses with chemicals is impossible. It is much easier and more reliable to prevent the disease by fighting herbivorous insects, which, as a rule, are carriers of pathogens - aphids, thrips, scale insects. But very often the infection is introduced in the greenhouse, before the plant goes on sale through the damaged fate of the roots or wounds on the stems and leaves.
All affected parts of the plant must be removed and destroyed. After work, wash your hands immediately thoroughly with soap, and wipe the equipment used with alcohol. Take cuttings only from healthy plants. In dry and hot times, the plant is shaded and sprayed more often.
Leaf spotting, similar to both fungal and bacterial or viral spotting, may not be caused by these diseases, but by nematodes.