
Plant dormancy is a condition in which no visible plant growth occurs. During the dormant period, most physiological processes in the plant are suspended, and some stop altogether. Obviously, the transition to a resting state is a consequence of the adaptation of plants to climatic changes in those regions where they grow in nature. The plant organism practically stops functioning, does not waste energy resources and is not damaged by exposure to low temperatures for a long time.
Plants distinguish between organic and forced rest.
Organic plant rest
Due to the hereditary properties of plants that have developed during evolution. These are the so-called endogenous (deep) plant processes programmed for each species, genus or family under the influence of climatic conditions. A number of such processes are unshakable and never violated.
There is such a science Phenology - studies and summarizes the totality of information about seasonal phenomena of nature, the timing of their occurrence and the causes of occurrence. The famous scientist, founder of the Moscow school of geobotany Vasily Vasilyevich Alekhin classified plants by the type of alternation of generative and vegetative phases into three groups: proant plants, mesant plants, and methane plants.
Proanthes are plants in which flowering occurs earlier than vegetation or at its very beginning, for example, cherries. Remember, in spring, there is not a single leaf on cherries yet, but they are all snow-white from flowers. Among indoor flowers is amorphophallus, and among greenhouses, the classic proant is amaryllis (not to be confused with hypeatrum). It flowers in a leafless state before growing. In addition to amaryllis, representatives of this group are among orchids: Pleione Pleione, or, for example, Calanta dressed Calanthe vestita.
Mesants are plants in which flowering occurs in the middle of the vegetation. These include most plants. They build up leaf mass and bloom at the same time. These are, for example, hibiscus, adenium, clerodendrum, jasmine, gardenia, azalea, anthurium and others.
Metants are plants in which flowering occurs at the end of vegetation. There are few such plants, among them, for example, poinsettia, cyclamens, many orchids (phalaenopsis, cymbidium and others). After fading, they have a dormant period.
To change endogenous processes, the plant needs a certain time, a certain temperature, moisture and lighting. When studying the life of plants in nature, scientists noticed that the transition from one state to another (from vegetation to rest and vice versa) manifests itself beforehand, some time before a sharp change in climate. So, plants of temperate latitudes begin to enter the resting phase long before the onset of real cold weather. If you grew such trees as bonsai, for example, long-shaped maple, you might notice: even if you transfer containers with plants to a warm room in the fall, the trees will not resume growing and do not start growing leaves, they will continue to enter the resting phase.
Short-term warming during the period of organic rest does not cause a transition to the vegetation phase. In rare cases, long-term climatic abnormalities can cause premature budding. And even in this case, the plants "swing" slowly, the speed of awakening is not the same as usual in spring. But the primary role in changing the phases of vegetation and rest is played by the genetic program inherent in a certain species and genus of plants .
In general, there are few plants in indoor floriculture, from temperate areas, for the reason that most of them are deciduous. And even conifers that can be grown as bonsai require very cold wintering and necessarily go into the phase of organic rest. But in the summer, such plants in apartments suffer - the air is too dry and warm for them, and therefore they live for a long time only in greenhouses.
Forced plant rest
Forced rest occurs in plants with a lack of favorable conditions for growth. This is primarily a decrease in light in winter and a decrease in temperature. If there is enough light and heat, then forced peace does not occur.
Many tropical plants grown as houseplants may well dispense with a dormant period. They are evergreen and in conditions of lower light in winter and cooler content (16-18 degrees) simply slow down growth. If the temperature drops below, to + 10-12 degrees, then the plants completely stop growing, but the processes of photosynthesis in most tropical plants stop when the temperature drops below 7 degrees.
I want to note that recently modern materials and technologies in the construction and arrangement of houses have significantly changed the wintering of our flowers on the windowsill. Remember the old wooden frames that had to be plugged and glued? Despite all efforts, they significantly reduced the temperature on the windowsill. It was 24-25 degrees in the room, 18-22 on the window. This was enough for the plants to survive the forced winter dormancy in conditions of short daylight hours and low light.
But now almost every apartment has plastic windows. And they hermetically close the window opening, reliably protected from blowing. The temperature on the windowsill is only 2 degrees lower than in the room. And only at the moments of ventilation it briefly decreases by 5-10 degrees. While on the street just above or just below zero, many people leave micro-ventilation. But as soon as the minus temperature is stably set, the windows are tightly closed for a longer time of day. But the illumination compared to the summer is significantly reduced.
All this leads to the fact that indoor flowers continue to grow, but due to a lack of light they lose a lot of decorativeness: shoots stretch out, leaves grind, grow frail and pale. In some cases, especially unpretentious pets can be radically trimmed in the spring, divided into children, taking away the strongest and most unpretentious... But some plants do not tolerate such strife between light (more precisely, darkness) and the dryness of the warm air of the rooms, and die.
Houseplants can be divided into three groups
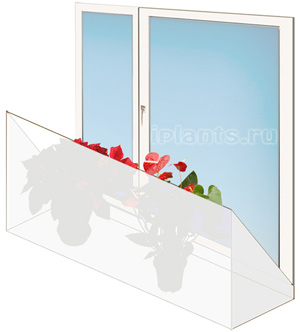 To protect plants on the windowsill from the hot air of batteries, you can make such a showcase (from glass, plexiglass or polycarbonate). The width (depth) of the showcase is equal to the width of the windowsill, and the height of the outer wall is at least 50 cm. Such a showcase allows you to reduce the temperature around the plants by 5-10 ° C compared to room temperature.
To protect plants on the windowsill from the hot air of batteries, you can make such a showcase (from glass, plexiglass or polycarbonate). The width (depth) of the showcase is equal to the width of the windowsill, and the height of the outer wall is at least 50 cm. Such a showcase allows you to reduce the temperature around the plants by 5-10 ° C compared to room temperature.- Plants, under favorable growth conditions, without a dormant period (tradescantia, cyperus, palm trees, croton, ivy, etc.). These plants can be found in winter under normal conditions, only it should be borne in mind that some loss of leaves and a slowdown in growth are natural with a decrease in illumination in winter.
- Plants that have a mandatory dormant period during the year (orchids, gloxinia, caladium, cypress, amarilis, myrtle, most cacti, etc.), which consists in a slight decrease in temperature and a decrease in watering. The temperature of the content varies greatly in different families and species. For example, there are cacti that need maintenance at + 5 ° C in winter, while others need + 12 ° C. Plants of this group painfully tolerate the absence of a dormant period. For them, it is needed to lay flower buds and bloom safely next season. In the absence of a dormant period, some plants may not bloom at all, while others simply die .
- Plants for which a resting state is not necessary, i.e. they may or may not have one. These plants can grow throughout the year (some dracenes, ficuses, syngonium, ferns, crinums, etc.)
Duration of rest period
Various external factors affect the duration of rest: temperature, soil moisture, lighting intensity, etc. Hereditary factors affect the duration of organic rest and the need of a plant for cold wintering.
For tropical plants under forced dormancy, the following dependencies are true:
Low ambient temperature lengthens the rest period, high - shortens it. Plant stripping is based on this.
The dryness of the soil lengthens the rest period, its moisture reduces it.
Intense lighting (increased illumination) also reduces the rest period.
In central Russia, climatic conditions are such that in winter daylight hours are shortened, it is not enough for good growth of natives of the tropics and subtropics. Therefore, most plants slow down vegetation and are ready for a period of rest. In this case, you should reduce the frequency of watering, lower the temperature in the room. The general conditions for keeping in winter for specific plants differ - all recommended indicators are given in the encyclopedia section for each plant. If it is not possible to lower the temperature, then you need to increase the illumination. Fluorescent lamps or LED lamps can be used for this. But to light up the plants not when it is convenient for you, but during the day, so that in total the daylight hours are 10-12 hours, this is from about 7 in the morning to 19 in the evening or from 8 in the morning to 18 in the evening.
Plants that are characterized by a mandatory dormant period (gloxinia, cyclamens, pomegranate) are best placed in a cool, dark basement, protected from drafts, but at the same time with enough fresh air. In city apartments, the place for wintering these plants will best be a bathroom (under the bathroom) or a staircase.
A sign of the end of the dormant period is the beginning of plant growth. If you have removed the pot with gloxinia cut off for the winter under the bath, then, looking there in the spring, you will find how shoots appeared from the ground - it's time to get the flower and place it in its usual place on the window. The organic (programmed) peace is over. The usual regime of watering and feeding is gradually resumed, if necessary, the plant is transplanted. If you do not get the plant and place it on the light, then the genetic program will still not allow it to "sleep" until better times. Growth will begin, but a few stunted leaves will grow, and then, in the absence of light, the plant will die.

Those plants that do not need a period of rest (violets, balsamine, cyperus, etc.) and are forced to winter on windowsills need to be watered and fed less during the month, when the shortest daylight hours. Winter-flowering pot plants that do not need a dormant period should be regularly watered and fed throughout flowering.
Problems of wintering indoor flowers
In fact, quite a lot of problems, diseases and death of plants occur in the winter months, when there should be a forced or mandatory period of rest. Mainly from violations of the conditions of detention: with a lack of light, not enough cool temperature, proximity of the heating system, too dry air, plants grow poorly, often stretch out, the stems are exposed in the lower part, flowering does not occur in spring.
If you do not want or cannot arrange a period of rest, balance the conditions so that the growth of the plant in winter is correct - so that there are no curved and small leaves and elongated shoots. To do this, first of all, you need to stop fertilizing with fertilizers and increase lighting using one or more fluorescent lamps.
After all, it is so simple - in any hardware store you can buy daylight lamps - within 300 rubles. A couple of screws in the wall and your plant over the winter not only will not lose its leaves, but it can bloom and delight the eye for a long time. However, this only applies to plants that do not need a mandatory dormant period.
Natalia Rusinova