Mulberry family. Ficus benjamina is one of the most common houseplants. In nature, it grows in India, China, South Asia, as well as in the Philippines, Hawaii, and Australia.
These are evergreen shrubs and trees. In nature, they grow like our birches, about 20-25 meters in height, at home, the ficus benjamin does not grow quickly and in about 10 years will reach 100-120 centimeters in height. Ficus has an invasive root system that spreads not only in depth, but also along the surface of the earth, the aerial roots of old plants growing in humid tropical climates form entire arrays of supports under a wide spreading crown. In indoor ficus in pots, the root system is quite strong, roots over time, if you do not add land, are shown above the surface of the earth, but aerial roots do not form.
Benjamin's ficus has dark gray bark, with brown transverse strokes. It branches very well, shoots drooping, leaves alternate, on short petioles, smooth, shiny, leathery, oblong (elliptical) or lanceolate, pointed at the end, 6-12 centimeters long and 3-6 centimeters wide. Fruits - syconia, about 1.5 centimeters in diameter, paired, axillary, red, maroon when ripe, inedible. In indoor conditions, the ficus benjamin does not bloom and, accordingly, does not bear fruit. On the petiole, when cutting the leaf, pruning the roots, sticky white milky juice is released.
Ficus benjamin varieties
Ficus benjamin has bred many varieties that differ in the shape, size and color of the leaf:
 Ficus benjamin variety Safari 'Safari'
Ficus benjamin variety Safari 'Safari'Small-leaved, leaves about 3-4 centimeters long, slightly bent by a boat along the central vein, the tip only slightly bent. The leaves are marbled in color: wide and frequent cream strokes and spots on dark green. It grows slowly. With a lack of light, it quickly loses its variegation.
 Ficus benjamin variety Barok 'Barok'
Ficus benjamin variety Barok 'Barok'The leaves are medium (about 4-6 centimeters), 3 times as long as wide. The leaf is bent in a ring along the central vein. It grows slowly, branches weakly, and several cuttings are planted in a pot to obtain a lush bush.
 Ficus benjamin cultivar Naomi Gold 'Naomy Gold'
Ficus benjamin cultivar Naomi Gold 'Naomy Gold'The leaves are large (about 6-7 centimeters), the leaf is 2-3 times longer than wide. The edge of the leaf is slightly wavy, practically not bent away, the shoots are thin, drooping, the bark is light. In the photo, the variegated form of this variety, in simple 'Naomy' the leaves are dark green and differ from the variety 'Monique' in the shape of the leaf - it is wider (not so elongated).
 Ficus benjamin Kinky variety 'Kinky'
Ficus benjamin Kinky variety 'Kinky'Small-leaved, the leaf has a length (about 4 centimeters) 2-3 times greater than the width. Leaves are straight, light green, cream or light green along the edge. Growth is moderate.
 Ficus benjamin variety Starlight 'Starlight'
Ficus benjamin variety Starlight 'Starlight'The leaves are medium (about 4-6 centimeters), 3 times as long as wide. The leaves are slightly bent by a boat along the central vein, the tip is only slightly bent, the edge is not wavy. The color of the leaves is saturated green with a wide white stripe along the edge, some leaves are almost white. Growing fast.
 Ficus benjamin variety Natasha 'Natasja'
Ficus benjamin variety Natasha 'Natasja'Small-leaved, the leaf has a length (about 3 centimeters) 3-4 times greater than the width. The leaves are slightly bent by a boat along the central vein, the tip is only slightly bent, the edge is not wavy. It grows slowly.
 Ficus benjamin cultivar Nicole 'Nicole'
Ficus benjamin cultivar Nicole 'Nicole'Small-leaved, the leaf has a length (about 4 centimeters) 3-4 times greater than the width. The leaves are slightly bent by a boat along the central vein, the edge is not wavy. The trunk is slightly zigzag (as in Wiandi), the shoots are directed upward. The leaves are light green with a wide cream border. Growth is moderate.
 Ficus benjamin variety Monique 'Monique'
Ficus benjamin variety Monique 'Monique'The leaves are large and the leaf is 3-4 times as long as wide. The edge of the leaf is wavy, practically not bent away, the shoots are thin, drooping. The variegate form with light light light green spots is also widespread. It's growing pretty fast.
 Ficus benjamin variety Vandy 'Wiandi'
Ficus benjamin variety Vandy 'Wiandi'Small-leaved, the leaf has a length (about 3 centimeters) 3-4 times greater than the width. The leaves are bent by a boat along the central vein, the tip slightly bent. The trunk is zigzag, has many creases - a change in the direction of growth, fragile. It grows slowly.
 Ficus benjamin variety Eldorado 'Eldorado'
Ficus benjamin variety Eldorado 'Eldorado'Very similar to Safari variety 'Safari', the difference is that El Dorado has larger leaves and wider ones. Leaves 5-6 centimeters long, twice as long. Growth is moderate or rapid.
 Ficus benjamin variety Carly 'Curly'
Ficus benjamin variety Carly 'Curly'The leaves are medium, about 4-6 centimeters long, twice as long, with a wavy edge, the tip is slightly bent away. The leaves are dark green with white spots, varying in size (large to small craps) usually from the petiole and leaf base, some shoots growing with completely white leaves. With a lack of light, the color is lost. It grows slowly.
Caring for ficus benjamin
Temperature
Moderate, optimal for growth in the range of 20-25 ° C, but by and large, the temperature of the ficus benjamin is unimportant, and it is important that the watering corresponds to the temperature - water more often when it is hot and less often when it is cooler. In cool conditions, a moist earthen lump dries slowly, for a long time and this is very harmful to ficus. In winter, ideally, the temperature should be 16-18 ° C, with a irrigation limit, the limit is 8-10 ° C with dry content. But usually the ficuses of benjamin grow perfectly in ordinary home conditions, in heated rooms. If there is little light, the plants partially lose their leaves, therefore, during warm wintering, ficuses can be illuminated, especially variegated varieties.
Lighting
Benjamin ficuses grow well in a bright place, with protection from direct sunlight at noon. The east window, where the sun happens in the morning or evening, is perfect. Variegated forms need a lighter and warmer place than forms with dark leaves. On the north window, only varieties with dark green leaves can grow well, and variegated varieties' Safari'or' Eldorado'need a west window to maintain color, or a place in the immediate vicinity of the south one is already dark on the east one.
Watering
Moderate, ficus does not like waterlogging of the soil, it must be dried well before the next irrigation. From waterlogging, the roots of the ficus benjamin can begin to rot, while the plant simultaneously throws off a large number of leaves, which lose their color, turn pale green. Water for irrigation is desirable soft, room temperature.
Fertilizer dressing
From March to August, every two to three weeks, you can feed the ficus benjamin with fertilizers for deciduous plants.
Air humidity
Leaves can be sprayed, especially in summer in hot dry weather, but Benjamin's ficus may well do without it, it tolerates the dry air of apartments well. But to wash off the dust from the leaves, you need to rinse the ficus foliage under a warm shower, while carefully protecting the soil from the stream of water.
How to transplant ficus benjamin
Transplantation is carried out annually in the spring, in fresh land. Old specimens are transplanted less often, every 2-3 years, but you can add fresh fertile land annually. The soil for ficuses should be loose and nutritious. This mixture is suitable: 2 parts of leafy land, 1 part of peat land, 1 part of sand and 1 part of well-decomposed compost. Leaf land can also be used in its pure form, ficuses grow well in universal soils from the store. Large, older specimens, which are less often transplanted, need heavier and more nutritious land - the main component is sod land 2 parts, leaf or greenhouse 1 part, you can add chopped pine bark, vermiculite and charcoal. An important condition is good drainage to the bottom of the pot, and the acidity of the soil should be slightly acidic, or close to neutral (pH 5.5-6.5). Alkaline and too acidic substrates ficus does not tolerate.
Pots can be ceramic and clay, they should not be too spacious, and in diameter 2-3 fingers wider than the root coma, or the pot in which the plant was bought. If it seems to you that the pot has become small (the roots seemed from the drainage hole), then the ficus benjamin can be transplanted again over the summer. If the roots are not cut or torn, then he tolerates the transplant well. After transplanting, refrain from watering, if not too hot for 2 days (if the house is very warm and dry, you can pour a little and spray the leaves).
Propagation of ficus benjamin
The easiest way to propagate ficus benjamin cuttings, they easily root in the water, in a bright place almost at any time of the year. Simply slice any sprigs you like about 13-15cm long, remove the bottom two leaves and place in a jar of clean water. To prevent water from blooming, cover the jar with opaque matter. Growth promoters are not needed. Cuttings of this size already have a woody stalk, but if you cut a couple of sheets with a still green stalk, it will not take root. Ficus benjamin does not reproduce with a leaf, and large branches with thick bark take an extremely long time to root.
If the plant for some reason bald in the lower part of the trunk, it is easier to re-root the crown. For this, not cuttings are used, but air extraction:
 Ficus Benjamin Air Tap
Ficus Benjamin Air TapThe bark is cut and removed on the trunk in the right place, a strip about 1 cm wide. The trunk in this place is wrapped with moss sphagnum wetted in water (it is fixed with a thread only for the convenience of photography)
Ficus crown formation
Ficus benjamin itself has a beautiful crown, many varieties do not require any special shaping. However, if the trunk of the ficus is exposed, the formation of new shoots and leaves by pruning can be stimulated. To do this, you can cut off part of the shoots, in whole or in part, sometimes it is enough to pinch the ends of the lower branches to start growing new buds. Pruning should be carried out in spring - early summer. The younger the ficus tree, the easier it is to form by pruning.
In addition to trimming and pinching, the crown of ficuses is formed by bending with wire (to form bonsai and pre-bonsai). Ficus shoots are quite flexible, easy to bend, but the thin bark can crack or break off the wire, so it is applied loosely, and braided wire is used. There should be a gap between the wire and the stems of the ficus - after all, the plant grows, and the branches gain thickness, with a dense winding, the wire will grow into the bark over time.
 Ficus Baroque is formed with wire, flexible ficus trunks can be bent quite abruptly, striving to achieve the chosen bonsai style.
Ficus Baroque is formed with wire, flexible ficus trunks can be bent quite abruptly, striving to achieve the chosen bonsai style.Cuttings of some varieties of ficus benjamin branch reluctantly, lonely twigs look and gain power slowly, can stretch upward, even with sufficient lighting, begin to branch, reaching about 30-40 cm in height. Therefore, it is worth pinching, cutting cuttings at a height of about 20 cm.
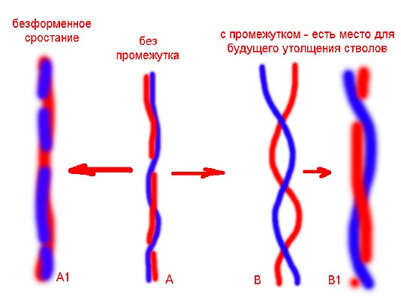
You can plant several cuttings in a pot and, if the stems are pressed tightly to each other, then in a very short time they grow together. You can bring the trunks of ficus cuttings together with the help of ordinary electrical tape - it is quite plastic, and does not injure the bark, stretches on growing trunks without growing. About once a month you need to inspect the braid, if necessary, rewind. It is better, of course, to fuse trunks of small diameter, 5-7 mm, but you can splice and thicker, only the process will take several years.
Another way of formation is to weave trunks with a pigtail or in the manner of a hedge - openwork weaving from the trunks of ficus benjamin. This method is suitable only for young flexible plants. At the same time, several large cuttings should be planted in one elongated container at a distance of 5 to 10 cm from each other strictly in a row. Initially, each trunk grows vertically and forms a die (all lower branches are removed). Approximately 20-25 cm high, ficuses can be fixed, tilted by crossing the trunks with each other. Fix with duct tape or jute.
Video: Benjamin's ficus shower
The video shows how to wash dust from ficus leaves and prevent the tick. What to pay attention to during this procedure.